Any good GMAT tutor provides a wide range of problem-solving strategies for the GMAT. While the GMAT is, as a general rule, a test of problem solving and critical...
Technical Mathematics on the GMAT - Part 2
In this article, we’re going to discuss best technical mathematics practices for the GMAT exam. You can either read this article or watch this GMAT technical mathematics video on YouTube. To make things easier to digest, we’ve broken the contents of the video up into 3 parts. In this article about technical math on the GMAT, hosted by one of MyGuru's most experienced GMAT tutors, we’ll work through a few different examples of technical mathematics in action. In part 1 of our three part series of technical mathematics on the GMAT, we discussed the frequency and format of technical mathematics questions and their strategic implications. If you haven’t yet read section 1 yet, we suggest you go back and make sure you understand that first. In part 3, we will provide a clear outline of the technical mathematics process.
Word Problem Example
If Abby travels 4 miles in minutes, and Barry travels 2 miles in b minutes, which of the following represents the number of minutes it would take Callum to travel 10 miles at the average of Abby’s and Barry’s rates in terms of a and b?
1. 2a+b
10ab
2. 2b+a
10ab
3. 2b+a
4. 10ab
2a+b
5. 10ab
2b+a
- To begin, create a scratch pad and list options A through E.
- Skip to the end of the problem to identify what is being sought, which is the number of minutes for c to travel 10 miles.
- Take notes from the beginning of the problem and set up equations as you go.
- Notice that the answer choices suggest that the answer should be an algebraic expression.
We can start with the formula: rate = distance / time = distance
time rate
- Average rate = 4/a+2/b
2
- Process fraction = 4a+2b
2ab
- Simplify fraction = 2a+b
ab
- Solve for times as t = 10
2a+b
ab
- Multiply by reciprocal, t = 10ab
2a+b
This matches choice E.
Make sure that you understand and find the technical approach to solving a problem straightforward. If you encounter difficulties, you can try another approach, but the technical method is usually the quickest and most efficient.
Arithmetic Example
Square root of ((27)(10)–(9)(15))
- 3√5
- 5
- 10
- 10√3
- 15
To begin, create a scratch pad with options A through E and use simple numbers. Arrange the choices in a format that is easy to manipulate to increase efficiency. You cannot estimate the answer; it must be solved using a technical approach until you get the final result. By examining the choices, you can see that the answer may be in square root form. This will guide our approach, which involves simplifying the roots by removing common factors.
- Ignoring the root sign 27 X 10 - 9X5
- 9 is a common factor 9 (3 X 10 - 1 X 5)
- Process parentheses 9 (30 - 5) = 9 X 25
- Put the radical back √(9-25) = 3 X 5 = 15
- Distribute radical 3 X 5 = 15
To solve this problem, you must use technical math; there are no other alternative approaches. If you become stuck in this kind of arithmetic problem, your best option may be to make an educated guess and continue quickly.
Geometric Example
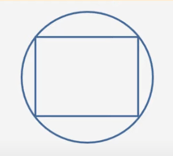
If the diameter of the circle above is 10, what is the area of the rectangle inscribed in the circle?
- 20
- 40
- 48
- 50
- 60
To begin, create a scratch pad with options A through E and use simple numbers. You do not need to draw the figure on your scratchpad. Jump straight to the conclusion of the problem and determine what value or values are being sought. Express the solution using mathematical formulas instead of relying on visual aids.
Area of rectangle = lw
Diameter = diagonal = 10
By Pythagoras theorem, diagonal2 = l2 + w2
Area of rectangle = lw
Diameter = diagonal = 10
By Pythagoras theorem, diagonal2 = l2 + w2
Pythagorean integers = 6 : 8 : 10
l = 6, w = 8, d = 10
Area of rectangle = 6 × 8 = 48
Conclusion
We hope this overview of the technical mathematics questions on the GMAT has empowered you to tackle these problems with newfound confidence. Remember to read part 3 of this article, where we will provide a clear outline of the technical mathematics problem-solving process.


